Melanoma starts when melanocytes become cancerous. Melanocytes come from the neural crest. This cancer can start in the skin. But, it can also appear in places where neural crest cells go, like the gut and brain.
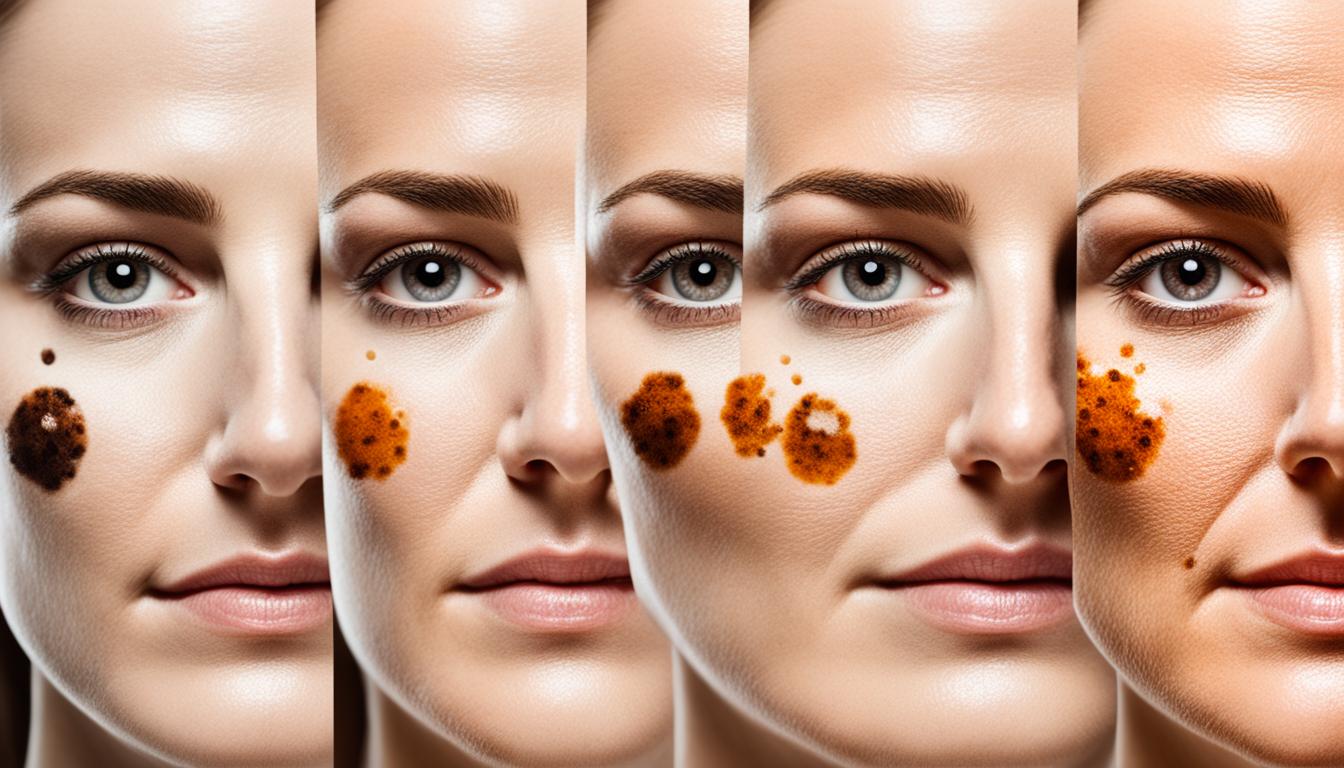
The survival chance after 5 years is 97% for stage 0 melanoma. For stage IV, it drops to 30%. Signs can show as a weird-looking, large spot that itches, bleeds, or grows new spots around it.
Factors like family history, fair skin, and getting too much sun can raise your risk. A biopsy is needed for diagnosis. Treatment depends on the cancer’s size, depth, and if it spread.
Key Takeaways:
- Melanoma is a malignancy derived from the malignant transformation of melanocytes.
- It can develop not only in the skin but also in other locations where neural crest cells migrate.
- Common symptoms of melanoma include the presence of an asymmetrical large lesion that may itch, bleed, ulcerate, or develop satellite lesions.
- Risk factors for developing melanoma include a positive family history, fair skin, sun exposure, and atypical mole syndrome.
- Stem cell therapy has shown promise in the treatment of melanoma.
Skin Cancer Types and Risk Factors
Skin cancer has many types. The most common are melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. Melanoma is the most dangerous. So, finding it early is really important.
Knowing the risk factors helps you protect your skin. Some risks are getting older, having had skin cancer before, or having a lot of moles. If skin cancer runs in your family or you have fair skin, you should be careful. Other risks include UV exposure and having certain diseases that weaken your immune system.
If you have these risk factors, take care of your skin. Check your skin often, wear protective clothes, and use sunscreen.
Some places have more melanoma cases than others. Australia and New Zealand have high numbers, according to the National Cancer Institute. Melanoma is the third most common cancer there.
Melanoma Awareness and Education
Melanoma is a big health concern. It’s important to know about it and how to prevent it. Public campaigns and good information can help save lives. They teach people how to spot early signs and get quick medical help.
Regular visits to the dermatologist are key. They help find skin cancer early. With everyone’s effort, we can beat melanoma.
Melanoma Prognosis and Research Breakthroughs
The chance of recovering from melanoma depends a lot on its stage when found. For those whose cancer is at stage 0 or is melanoma-in-situ, the 5-year survival rate is 97%. But for stage IV melanoma, the rate drops to just 30%. This shows how vital early detection and treatment are.
Thanks to recent research, we have exciting new ways to fight melanoma. There are new mixes of targeted drugs and special types of immune therapies. These have greatly helped people with advanced melanoma live longer and better lives.
Significance of Research Breakthroughs
Only about 4% of melanomas spread by the time they’re found, says the American Society of Clinical Oncology. This shows the big chance for curing melanoma if it’s found early. More research into melanoma aims to make treatments even better and improve patient outcomes.
Now experts are working on medicines that fit each patient’s unique genetic makeup. They look at the genes that make the melanoma spread. Then they make treatments that target these genes. This approach can be very effective with fewer bad side effects.
Researchers are also looking into cool new treatments, like adoptive cell transfer and immune checkpoint inhibitors. With adoptive cell transfer, they change a patient’s immune cells to fight the cancer. Immune checkpoint inhibitors help the immune system fight cancer better. Sometimes, these treatments keep working well in some patients for a long time.
All these new discoveries are really promising for beating melanoma and making treatments better. With more progress, we hope to win the fight against this serious disease.
Illustration for demonstrative purposes only: Image depicting a melanoma research study.
Advances in Stem Cell Therapy for Melanoma
Stem cell therapy is becoming a hopeful option for melanoma, a dangerous skin cancer type. It explores how stem cells might attack melanoma cells and help the body fight cancer better.
This method shows promise in better managing and treating melanoma. Stem cells could find and kill cancer cells, leading to more personal and precise treatment plans.
Current studies and trials aim to understand and improve stem cell therapy for melanoma. Researchers are looking for ways to develop more precise and efficient treatments against this severe cancer.