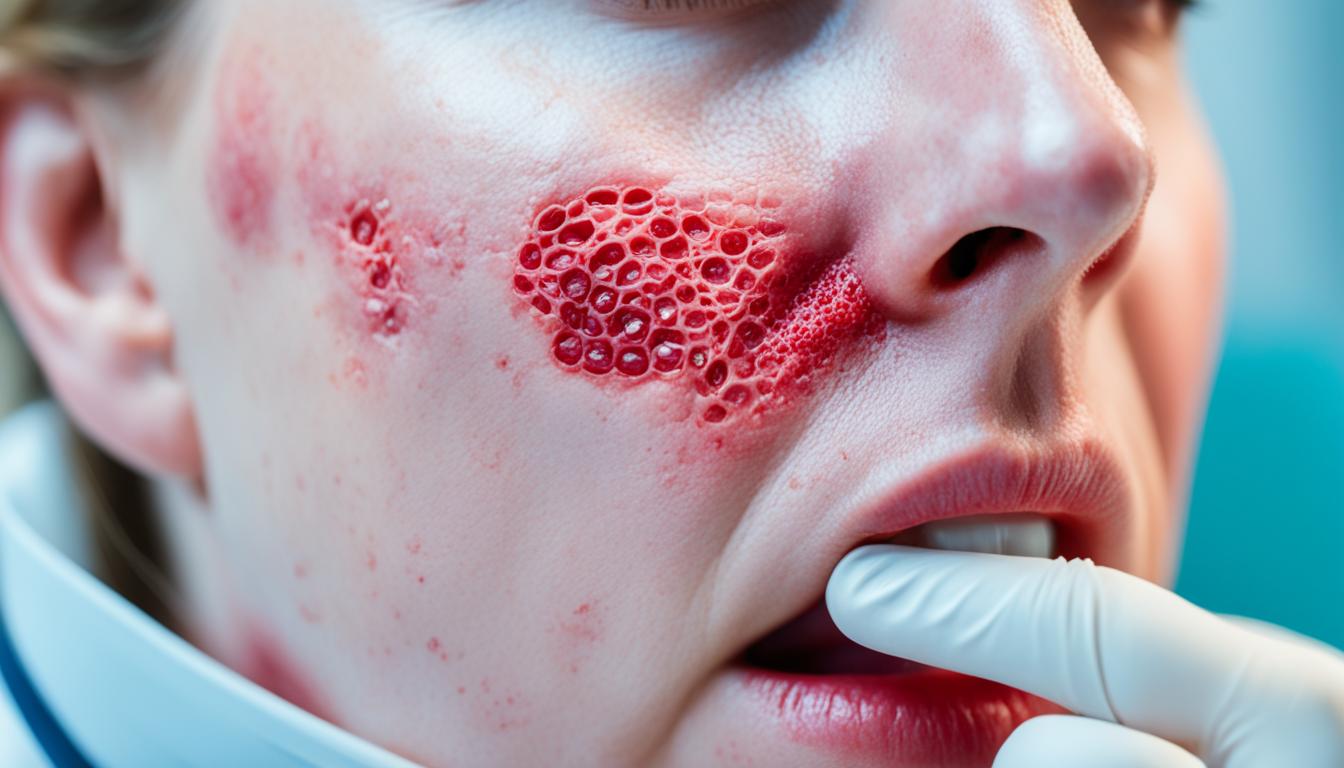
Rosacea is a long-term skin issue that mainly affects the middle of the face. It shows signs such as face turns red, redness, and skin bumps that look like pimples. The exact cause of rosacea is not known for sure. But it may happen because of problems in the immune system, facial blood vessels that overreact, and reaction to germs, which causes an inflammation. It’s also linked with genetics. Things like the sun, stress, warm days, intense workouts, drinking alcohol, and eating spicy foods can make rosacea worse.
Doctors usually diagnose rosacea by looking at your skin. Unfortunately, there’s no complete cure for it yet, but you can make it better with several treatments. These include using laser therapy, skin medicines such as brimonidine gel and oxymetazoline cream, and taking antibiotics by mouth. Changing your habits to avoid your personal triggers along with good skin care can also reduce these symptoms. One interesting area of research is about using stem cells to treat rosacea. This method shows hope for effectively dealing with the disease.
Key Takeaways:
- Rosacea is a chronic skin condition characterized by facial flushing, redness, and pimple-like bumps.
- The exact cause of rosacea is unknown, but factors like immune system dysfunction and genetic predisposition are thought to contribute to its development.
- Flare-ups of rosacea can be triggered by sun exposure, emotional stress, hot weather, exercise, alcohol, and spicy foods.
- Diagnosis is usually based on clinical examination, and various treatments like laser therapy and topical medications can help manage symptoms.
- Stem cell therapy is an emerging treatment option with potential benefits for rosacea patients.
Types of Rosacea and Their Characteristics
Rosacea is a skin issue with different types, each showing unique features. These types are Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea, Papulopustular rosacea, Phymatous rosacea, and Ocular rosacea.
Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea
This type shows as constant redness and visible blood vessels on the face. People with it might flush easily and have facial sensitivity. The redness is often on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin.
Papulopustular Rosacea
Known as acne rosacea, this type has small red bumps and pimples on the face. It often comes with constant redness. Even though it looks like acne, they are really different things.
Phymatous Rosacea
This type makes the skin thicken, mainly on the nose. It can make the skin bumpy and can even enlarge and deform the nose. Sometimes other areas also get thickened skin. While seen most with this type, a bumpy nose can happen in others too.
Ocular Rosacea
Ocular rosacea involves the eyes and can lead to burning, dryness, and other symptoms. Eyelid inflammation and swelling are common. This can make the eyes look watery or bloodshot.
| Subtype | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea | Persistent redness, visible blood vessels, facial flushing |
| Papulopustular Rosacea | Pimple-like bumps, redness, inflammation |
| Phymatous Rosacea | Skin thickening, bumpy texture, rhinophyma |
| Ocular Rosacea | Eye symptoms, burning, stinging, redness, photophobia |
It’s key to correctly diagnose the type of rosacea for the best treatment. A doctor can look at the symptoms and suggest an effective way to handle the condition.
Treatment and Management of Rosacea
Treating rosacea means thinking about its type and how bad it is. Laser therapy often helps lessen the look of blood vessels and redness. It’s a simple process that uses intense light on the skin’s problem areas.
Alongside laser therapy, topical medications are key in dealing with rosacea. For instance, brimonidine gel and oxymetazoline cream reduce redness and soothe the skin. Medicines like metronidazole gel/cream, ivermectin, and azelaic acid help calm the skin by reducing swelling.
If rosacea gets bad, oral antibiotics might be needed, mainly for papulopustular rosacea. These pills help control skin inflammation and beat back bacteria. Sometimes, a course of these pills followed by ongoing therapy can deal with the problem.
But, it’s not just medicine that helps. Changing your way of life can also make a big difference in managing rosacea. Stay away from things that set it off, like too much sun and certain foods. A simple, gentle skin care routine with soft products can help keep your skin in good shape. And, talking to your doctor about stem cell therapy might also be a good idea. It has the promise to help repair the skin.