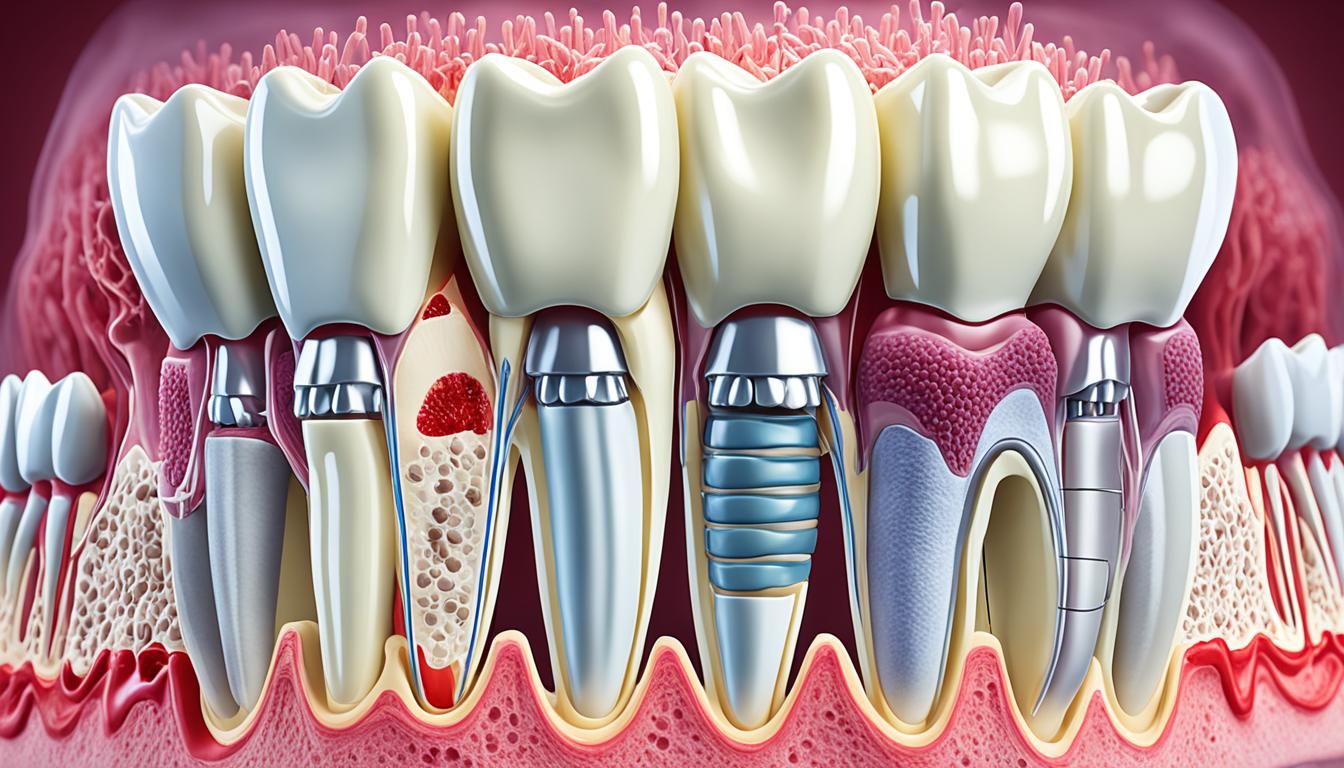
Periodontal disease, or gum disease, is a common issue that harms the teeth’s support. It starts with gums getting inflamed (gingivitis). Later, it turns serious if not treated. The main reason behind it is not keeping your mouth clean. This lets bacteria, forming a sticky film called plaque, to grow on teeth and gums. Smoking, diabetes, changes in hormones, and some meds also play a role in getting this disease.
The signs of periodontal disease are easy to spot. Your gums become red, swollen, and can bleed. You might also have bad breath and feel like your teeth are coming loose. A dentist can confirm if you have it through a check-up and X-rays. The fix includes deep cleaning, taking antibiotics, or even having surgery.
Stem cell therapy is now a new hope for treating periodontal disease. Scientists are finding that stem cells from parts of your teeth can help heal your mouth. This might mean less damage to your teeth and gums if you have this disease.
Key Takeaways:
- Periodontal disease hurts the gums and support around teeth.
- Not keeping your teeth clean is the main reason for it.
- Its signs are easy to see – red, swollen gums, bad breath, and loose teeth.
- Dentists can find it by looking at your mouth and taking X-rays.
- Fixes include deep cleaning, medicine, or surgery.
- Using stem cells might be a good way to treat it in the future.
The Role of Bacteria and Inflammation in Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease’s growth is affected by both the oral bacteria and the body’s reaction. The mouth has many bacteria types, which build layers on teeth and gums. If this balance breaks, periodontal disease can start.
Bad bacteria cause an immune response in the mouth, impacting gum, and bone health. This leads to gum and bone damage, which can make you lose teeth if not treated.
Periodontitis often shows no symptoms until it’s advanced. At that point, you may see signs like loose teeth or bad breath. Addressing specific bacteria and managing inflammation are key to fighting this disease.
Key Factors in the Development of Periodontal Disease
| Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Oral Microbiome | |
| Periodontal Bacteria | Bacteria present in the periodontal pockets |
| Chronic Inflammation | Long-term inflammation in the gums and periodontal tissues |
| Immune Response | Body’s response to the bacterial infection |
| Periodontal Tissue Destruction | Breakdown of gum and bone tissues |
The oral biome and the immune system’s response are important in periodontal disease. This knowledge helps scientist and dentists create ways to fight, manage, and heal periodontal disease.
Stem Cell Therapy for Periodontal Regeneration
Regenerative medicine is making headway in fighting periodontal disease. This is a common problem in oral health. Stem cell therapy is getting known for helping new tissue grow and fixing damaged gums and teeth. Stem cells from parts like the gum tissue and tooth pulp have shown they can rebuild the structures around teeth.
The unique thing about these stem cells is they can become many other cell types. This includes cells that make up bone or the stuff that supports teeth. This process helps in healing the damage around teeth.
Also, these stem cells have a special effect on the immune system. They can help control the body’s reaction to unhealthy gums and teeth. This means they might help in stopping the harmful effects of long-term gum problems.
With new research, we could better understand how to use stem cells for gum health. These findings offer a bright future for treating gum disease. They might even improve how we care for our mouths.