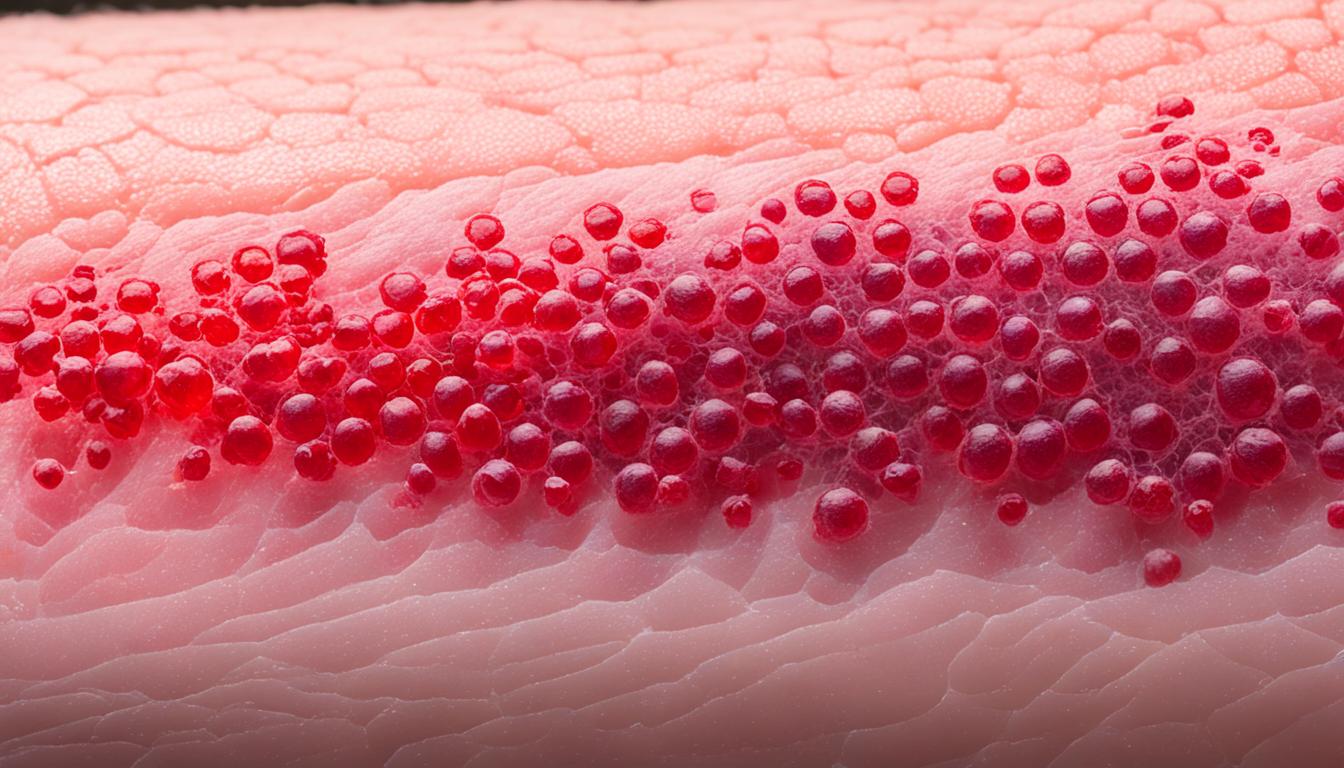
Chronic hives, or chronic urticaria, makes the skin itch and form wheals. It impacts 1-3% of the world’s people, mostly women. The exact reason for this disease is not totally clear. It is possibly linked to immune reactions related to autoimmune problems, allergies, and other health issues.
To diagnose chronic hives, doctors will look at your medical past and give you a check-up. Sometimes they might do blood tests or take samples from your skin. While there’s no cure, you can manage its effects. Treatments include taking antihistamines, corticosteroids, or drugs that lessen immune reactions.
Stem cell therapy is being looked at as a new way to treat chronic hives. It involves using special cells called mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) to calm down the immune system and help skin repair itself. Early tests look good. But, we need more research and tests to be sure stem cell therapy is safe and helpful for chronic hives.
Key Takeaways:
- Chronic hives makes your skin itch and form raised bumps.
- It’s more common in women than men.
- Health problems like autoimmune issues or allergies might start chronic hives.
- Diagnosis usually needs checking your medical history and a physical exam, plus sometimes extra tests.
- Managing chronic hives includes using antihistamines, corticosteroids, or immune-suppressing drugs.
- Stem cell therapy, with MSCs, looks like it could be a good treatment option.
- We need more research to know if stem cell therapy is a safe and effective way to treat chronic hives.
Causes and Pathophysiology of Chronic Hives
Chronic hives can start due to many reasons, with a mix of complex factors behind them. The exact causes of chronic hives aren’t fully known yet. But, we do know a few things that might trigger or contribute to them.
Autoimmune Dysfunction: Autoimmune dysfunction might be behind chronic hives. Here, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy parts of the body. This attack leads to the release of histamine and other chemicals. This, in turn, causes hives. Conditions like lupus and thyroid diseases could be linked to chronic hives.
Allergic Reactions: Allergic reactions can also cause chronic hives. Things like certain foods, medications, insect bites, and what’s in the air can trigger them. When the body comes in contact with these, it releases histamine. This leads to the hives’ itching and redness.
Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain health issues can also lead to chronic hives. Conditions like thyroid problems, autoimmune diseases, and some infections might cause them. It’s important to find and treat these conditions to manage chronic hives well.
The process behind chronic hives includes active mast cells. These cells are key in hives’ development. Once stimulated, they release histamine and other chemicals. This causes the skin to swell, itch, and turn red.
Treating chronic hives means finding and tackling their root cause. This includes avoiding known allergens. Doctors also use medicines like antihistamines and corticosteroids. These drugs help control the immune system and reduce redness and itching.
Common Causes of Chronic Hives:
- Autoimmune Dysfunction
- Allergic Reactions to Certain Substances
- Underlying Medical Conditions
Knowing what causes chronic hives and how they work is key to making effective treatments. This is vital for easing the lives of people dealing with this ongoing issue.
Stem Cell Therapy for Chronic Hives
Stem cell therapy, using MSCs, is a new way to treat chronic hives. These cells can change how the immune system works and help in healing. Tests on animals and people have shown good outcomes.
Studies suggest MSCs can reduce swelling, lower the release of substances like histamine, and balance the immune system. They also have the power to help in regrowing tissues. This might offer some relief from hives and stop them from coming back.
But, we need more studies to understand how MSC therapy works and its long-term effects on chronic hives. Trials are looking at how safe and useful MSCs are for treating allergic and immune diseases. They also aim to figure out the best way to give this treatment.
Stem cell therapy could change how we deal with chronic hives. As we learn more, using MSCs might lead to better ways to handle this problem. This could make life better for those with chronic hives.