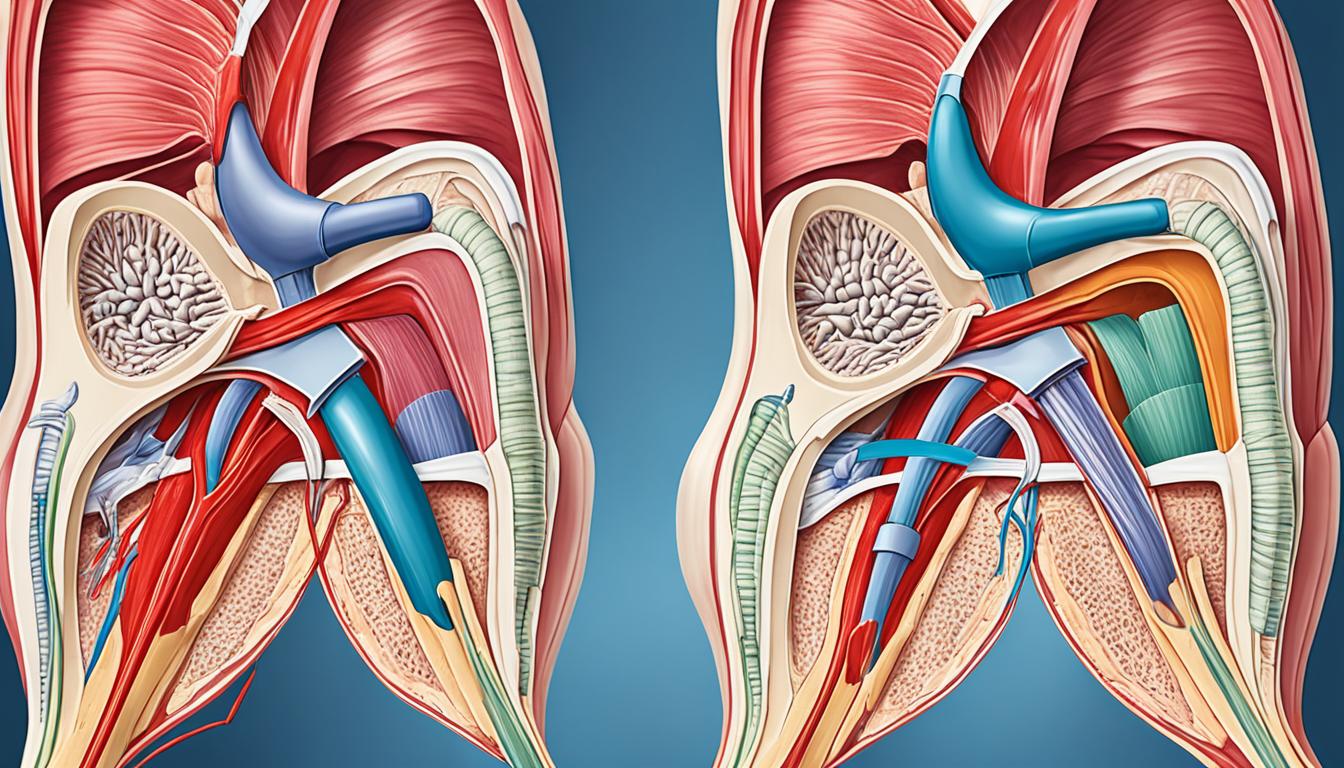
A hernia is a common health issue. It happens when organs or tissues push out through the muscle walls of the abdomen. Various hernia types include femoral, inguinal, hiatal, and umbilical. Inguinal hernias are the most seen in men. This is when parts of the intestines or fatty tissue push into the area around the groin or inner thigh. These are much less common in women.
Several factors can cause hernias. These include age, gender, family history, chronic coughing, and obesity. Symptoms of an inguinal hernia can be quite obvious. You may see or feel a lump in the groin. This might go away when you lay down. Someone with this issue might feel like their bowel is blocked or very full. There can also be mild to severe pain.
Treatment for this kind of hernia varies. It could be watchful waiting, laparoscopic or open surgery, or robotic repair. It’s key to seek treatment because an untreated hernia can lead to serious problems. These include obstruction or the tissue being strangled.
Key Takeaways:
- Inguinal hernias occur when organs or tissues push through the abdominal wall muscles into the groin area or inner thigh.
- Common symptoms include a noticeable lump or bulge in the groin area, discomfort, and a sense of fullness or bowel obstruction.
- Treatment options for inguinal hernias include watchful waiting, surgery, and robotic hernia repair.
- Complications of untreated hernias can include obstruction and strangulation, which may require emergency medical intervention.
- Consultation with a general surgeon or gastrointestinal surgeon is recommended for proper evaluation and management of inguinal hernias.
What is an inguinal hernia?
An inguinal hernia happens when an organ or intestine bulges through the abdominal wall. This bulging occurs in a spot called the inguinal canal. It’s more often seen in men, where the groin or inner thigh area is affected.
Other hernias can also show up. These include femoral hernias that push into the thigh, hiatal hernias that move parts of the stomach into the chest, and umbilical hernias near the navel. These different hernias each have their own unique area they affect.
| Type of Hernia | Location |
|---|---|
| Inguinal Hernia | Groin area or inner thigh |
| Femoral Hernia | Inner thigh muscles |
| Hiatal Hernia | Chest cavity through the diaphragm |
| Umbilical Hernia | Near the navel area |
Complications of inguinal hernia
Inguinal hernias, if not treated, can cause severe problems. These issues can lead to pain and discomfort. They can lower the patient’s quality of life too.
Inguinal hernias happen when organs push through the abdominal wall. This usually occurs at the inguinal canal. If these organs stay outside the abdomen, it causes problems.
Strangulation is one serious issue. It happens when the herniated organ gets stuck. If this continues, the organ does not get enough blood. This problem can cause the organ to start dying because it lacks oxygen and nutrients. This condition, called organ necrosis, is a medical emergency.
If an inguinal hernia is left alone, there is also a higher risk of infection. When the organ is outside, it is open to bacteria. Infections can make the situation much worse, leading to more health problems.
Quick treatment is key to avoiding these harmful complications. Surgery is often needed. It aims to fix the hernia and make the abdominal wall stronger. Getting surgery in time can stop problems from getting worse. It also lowers the chance of the hernia coming back.
Conclusion
Inguinal hernias are common and need early attention. Watch for signs like groin bulges, pain, and discomfort. Getting treated without delay can avoid problems and better results.
Surgery is often needed to treat inguinal hernias. It can be done openly or through tiny cuts with a camera. The aim is to fix the hernia and strengthen the belly’s wall. Always talk to a doctor, like a general or gastrointestinal surgeon, for the best care.
Getting the right treatment can improve life and cut down on risks. If you think you have this problem, see a doctor. They can help you make a plan for your health.