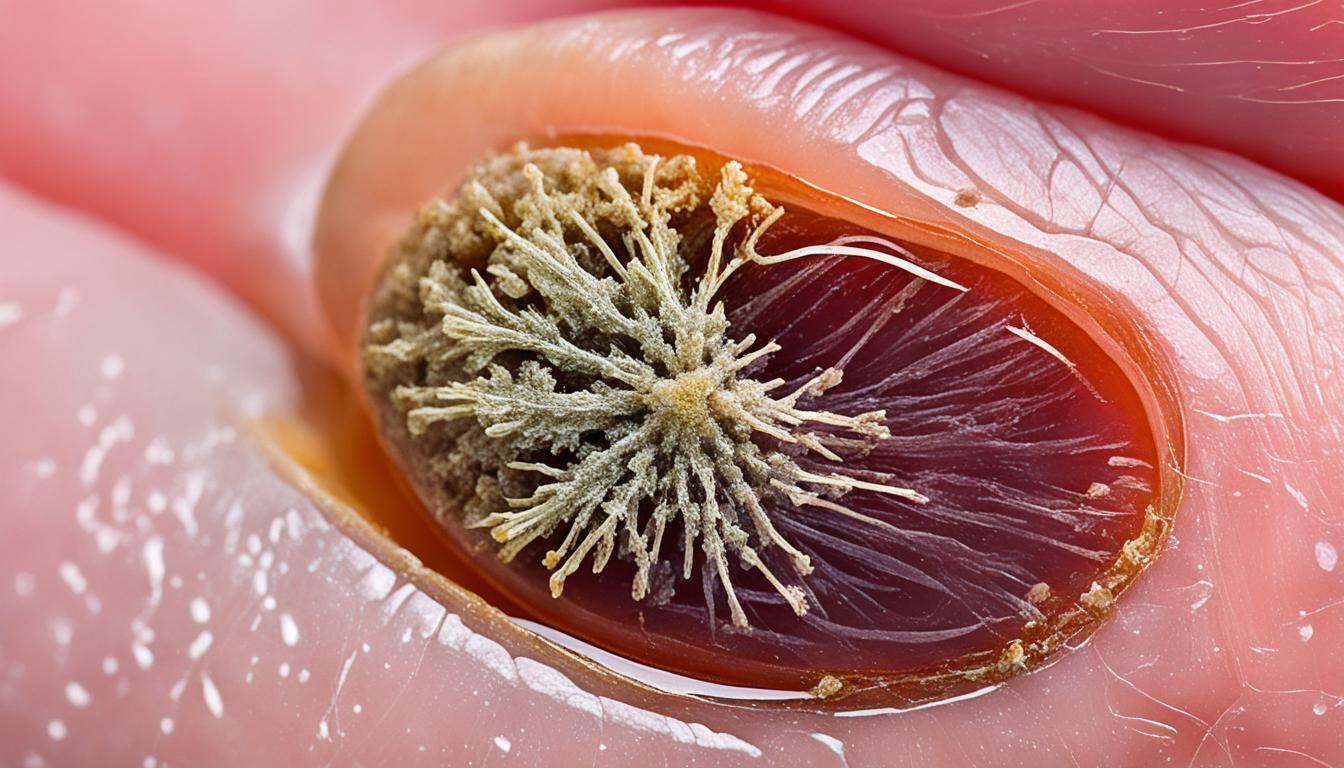
Fungal nail infections, known as onychomycosis, affect up to 14% of people. They happen more with toenails than fingernails.
Signs of a fungal nail infection are nails that are discolored, thick, fragile, or split. Sometimes the nail separates from the bed. It can also be linked to skin fungal infections like athlete’s foot.
The main reason for fungal nail infections is contact with fungi from the environment. This can happen through small openings in the nails or nearby skin. Things like nail injuries, deformed feet, diabetes, a weak immune system, and skin fungal outbreaks increase the risk.
Preventive steps involve keeping nails short and clean, not walking barefoot in public places, and not sharing nail tools.
Doctors typically diagnose fungal nail infections with lab tests. Treatment might include antifungal pills, nail removal in severe cases, and managing linked skin fungal problems.
Scientists are looking into using stem cell therapy for fungal nail infections.
Key Takeaways:
- Onychomycosis mainly targets toenails and is more common than fingernail fungal infections.
- Symptoms are thick, discolored, fragile or cracked nails with separation from the bed.
- It’s usually caused by fungi in the environment that enter through tiny nail or skin breaks.
- To prevent, keep nails short and clean, don’t walk barefoot in public, and avoid sharing nail tools.
- Doctors use lab tests to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment includes antifungal drugs, sometimes nail removal, and managing skin infections.
Types and Complications of Fungal Infections
Fungal infections, or mycosis, can hit the skin, nails, mouth, throat, lungs, or urinary tract. Unlike plants and animals, fungi spread by spores. Only a few of the many types can make people sick.
Fungal infections come in two main types. Some stay on the skin, nails, and mucous membranes. Others dive deeper, affecting organs like the lungs, brain, or heart. Here are a few common ones:
- Ringworm
- Onychomycosis (fungal nail infection)
- Candidiasis
- Tinea versicolor
The severity of these infections varies. They can be mild or even life-threatening. People with weak immune systems are at higher risk. For example, those who’ve had stem cell transplants face a greater risk.
It’s key to diagnose and treat these infections early. This can help avoid serious complications and ensure the right care.
Complications of Fungal Infections
Fungal infections might lead to several problems. The type and severity of the infection matter. Here are some possible complications:
- Spread of infection to neighboring tissues
- Secondary bacterial infections
- Persistent or chronic infections
- Allergic reactions
- Fungal meningitis
- Life-threatening invasive fungal infections
People with weakened immune systems face more risks. Quick, proper treatment helps prevent the infection from worsening. And it can stop severe complications.
Stem Cell Transplants and the Risk of Fungal Infections
Stem cell transplants can mean a new lease on life, using either the patient’s or a donor’s stem cells. Yet, they come with a higher chance of getting fungal infections.
For those receiving stem cells from a donor, known as allogeneic transplants, the risk is even greater. This is because they must take medicines that lower their immune system. This makes them more susceptible to fungal infections. Also, the treatment process like chemotherapy and radiation can reduce the body’s ability to fight off infections even more.
Graft-versus-host disease, where the new immune cells attack the host, adds to the risk. The common fungal infections after these transplants are aspergillosis, Candida, and mucormycosis. Catching these early and treating them is key to prevent serious problems. It’s important for patients to watch out for any unusual symptoms and talk to their doctors if symptoms get worse.
Some might get antifungal medicines to keep the infections away. Yet, everyone should learn about fungal infections and how to avoid them. This includes seeking extra medical help when needed and being careful to not pick up fungal diseases from the environment.