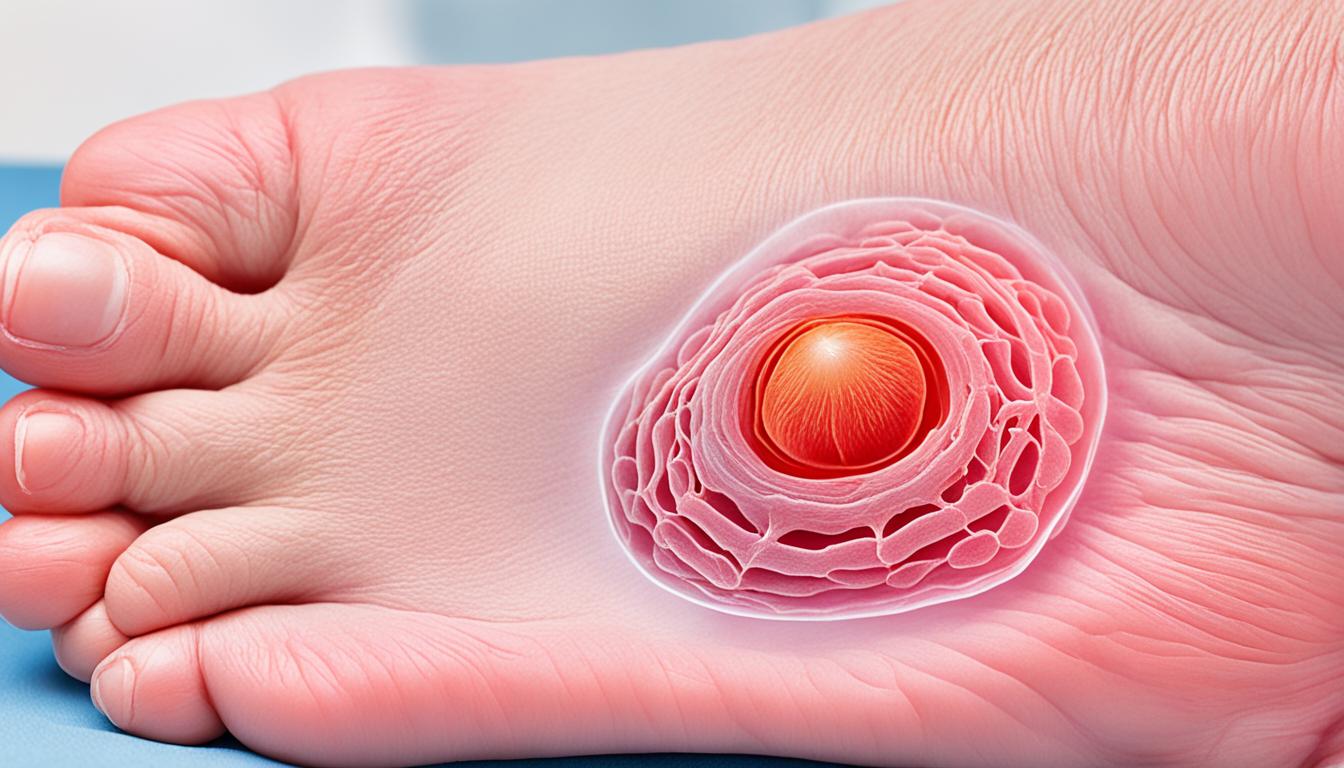
Ganglion cysts are common and often filled with a jelly-like material. They are most often seen in the hand and wrist areas, but can appear in the knee and foot too. Most of these cysts don’t cause any problems, but some people find them painful or experience weakness. The cause of these cysts isn’t completely understood, but we know they might come from repeated, small injuries. These cause a kind of tissue change. While you can get surgery to remove them, they often come back. Now, stem cell therapy is showing it might help people with cyst ganglion disease.
Key Takeaways:
- Ganglion cysts are synovial cysts filled with gelatinous mucoid material.
- They primarily occur in the hand and wrist but can also be found in the knee and foot.
- Most ganglion cysts are asymptomatic, but some patients may experience pain or weakness.
- The exact cause of ganglion cysts is unknown, but repetitive microtrauma plays a role.
- Non-operative and surgical treatments are available, with stem cell therapy showing promise.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Cyst Ganglion
Ganglion cysts are often found in the hand, wrist, or foot. You can usually see a lump under the skin where they are. Although they are often without symptoms, sometimes they can cause issues.
People might feel pain, a tender spot, or not as strong as usual near the cyst. Moving the wrist a lot might make these problems worse. Rarely, these cysts can press on nerves, making the area feel tingly or numb.
To diagnose a ganglion cyst, a doctor will do a full check-up and ask about your health history. They might also order tests like X-rays or MRIs to be sure of the diagnosis and to rule out other problems.
Diagnostic Techniques
X-rays help in spotting any bone issues or other causes for your symptoms. MRIs give a more extensive view of the cyst and what’s around, helping in making the right diagnosis.
Ultrasounds can also be used. They help tell if it’s really a cyst and not something else. This is very useful when a doctor plans to drain the cyst to avoid hitting important spots like the radial artery.
It takes physical checks, looking at your health history, and using the right tests to diagnose a ganglion cyst. Knowing the signs and symptoms helps doctors make a plan to treat people with these cysts.
Treatments for Cyst Ganglion
The way cyst ganglion is treated depends on how severe it is and what the patient wants. Sometimes, the best course is to wait and see what happens. Cysts that don’t cause any symptoms might simply go away. For those in pain, a splint can help by keeping the joint still, reducing irritation.
Another choice is aspiration, which means pulling the liquid out with a needle. This can make the pain better, but the cyst might come back. Doctors usually suggest this for cysts that really hurt or affect the way you move.
If surgeries are needed, the doctor will completely take out the cyst. They make sure not to harm any nerves or blood vessels nearby. This helps the patient move and feel better after the surgery.
Even after a cyst is removed, it might come back 15% to 20% of the time. But, there’s a new method that holds hope. Stem cell therapy can use a person’s stem cells to fix the area. It could stop more cysts from forming, making it a good long-term solution.