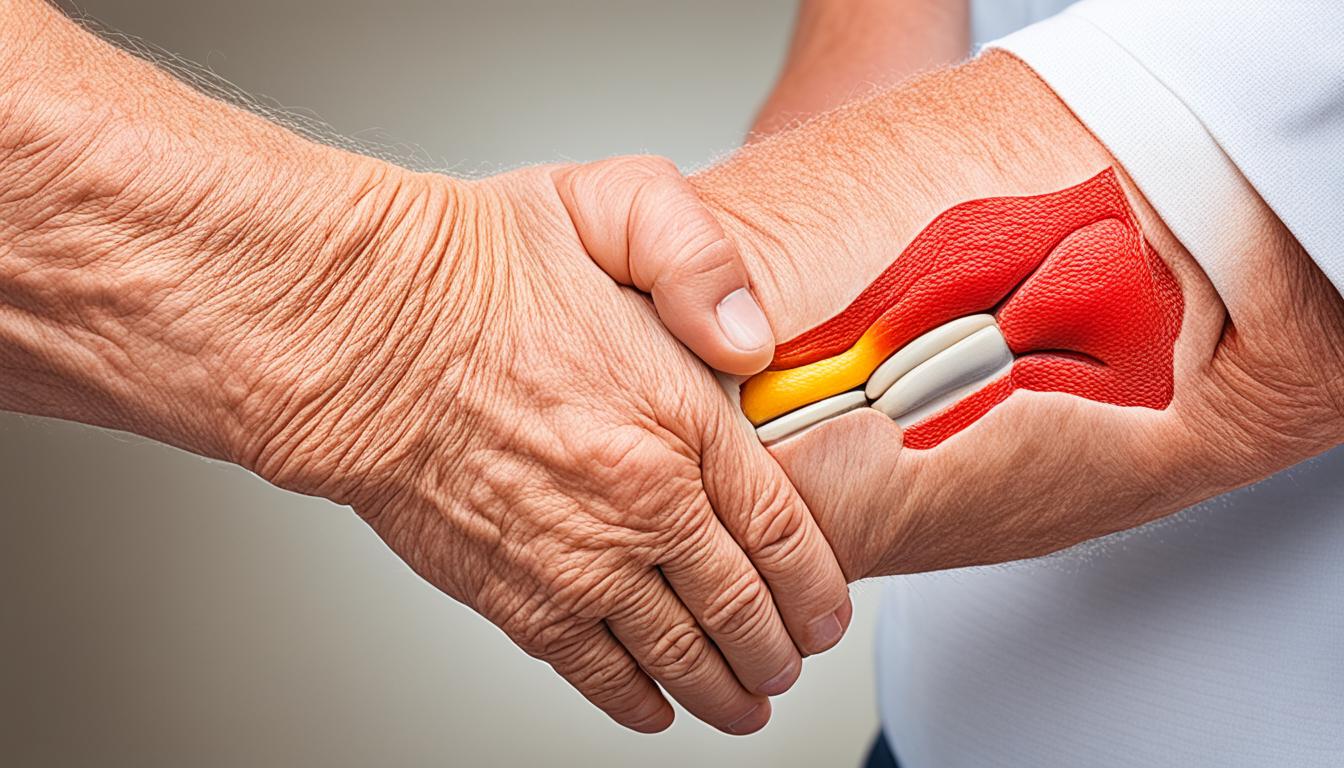
Arthritis osteoarthritis is a common joint disease. It affects millions of people all over the world. It causes joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. This makes it hard for people to move well. The knees, hips, spine, and hands are often hit hard. This condition can make life less enjoyable by limiting what you can do every day.
By 2019, about 528 million people were dealing with this condition. That’s a 113% increase since 1990. It usually affects the knees first, then the hips and hands. Age, injuries, being overweight, and some health conditions increase your risk. Getting diagnosed early and the right treatment can help a lot.
We will look at the signs, reasons, how it’s found, and ways to treat arthritis osteoarthritis. We’ll see how stem cell therapy might help too.
Key Takeaways:
- Arthritis osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint condition that causes pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- The global prevalence of osteoarthritis has increased by 113% since 1990.
- The knee is the most commonly affected joint, followed by the hip and hand.
- Risk factors for developing osteoarthritis include age, joint injuries, obesity, and certain metabolic diseases.
- Stem cell therapy is a promising field of research for the management of osteoarthritis.
What is Arthritis and How Does it Manifest Itself?
Arthritis is not just one disease but a group of them. They all affect the joints and the cartilage. The most common types are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis makes the cartilage thin, which leads to pain and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is when the body attacks its own joints. This causes them to swell, be painful, and stiff.
People with arthritis can feel joint pain, see their joints swell or be red, and have a hard time moving. They may also feel tired, have a fever, or lose weight. But, these symptoms can change from person to person, based on the type and the seriousness of their arthritis.
An arthritis treatment plan includes medicine to lower pain and swelling. Physical therapy and certain exercises are good for joint movement and muscle strength. A diet with anti-inflammatory foods could also help reduce symptoms. Remember, seeing a doctor is crucial. They can help you with the best plan for your condition.
If the arthritis is very bad, sometimes surgery is needed. For example, joint replacement could be necessary. But, this is usually done when other options don’t work.
Understanding Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Osteoarthritis happens a lot because of joints being used for a long time. It damages the cartilage that’s between bones. When this protective layer wears off, bones start to rub against each other. The result is joint pain, stiffness, and less movement.
Rheumatoid arthritis is different. It’s an attack by the immune system on the body’s own joints. The attacked area swells and can be damaged, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Arthritis is usually a long-term problem. But, it can be managed with the right care and treatment. This way, people with arthritis can still enjoy their lives and keep the negative effects of the disease at bay.
Types of Arthritis and the Danger of Arthritis
Arthritis comes in many forms, with different symptoms and causes. Types include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and more. Arthritis can lead to severe joint damage and disability if not treated. It’s important to take steps to prevent or lower the risk of arthritis.
- Arthritis Prevention: Keeping a healthy weight helps prevent arthritis, especially osteoarthritis. Extra weight stresses joints, causing more damage. It’s also important to exercise to keep your joints strong and flexible. Talk to a healthcare provider for an exercise plan.
- Osteoarthritis Relief: If you already have osteoarthritis, there are ways to manage it. Exercises like swimming and cycling can reduce pain and improve motion. Therapy helps with daily activities that may strain your joints.
Danger of Arthritis
Untreated arthritis can cause permanent joint damage and disability. For example, osteoarthritis wears down joint cartilage. This leads to chronic pain and limits motion. But, early lifestyle changes and medical care can lessen arthritis risks. This can improve your life significantly.
Acting early to prevent and treat arthritis can keep your joints healthy. This approach reduces the condition’s impact.
Common Types of Arthritis
| Type of Arthritis | Symptoms | Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis | Pain, stiffness, reduced range of motion | Age, joint injuries, obesity |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | Joint inflammation, pain, swelling | Autoimmune disorder |
| Psoriatic Arthritis | Joint pain, swelling, skin psoriasis | Immune system dysfunction, genetic factors |
| Gout | Severe joint pain, redness, swelling | Uric acid crystal buildup |
| Lupus Arthritis | Joint pain, swelling, fatigue | Autoimmune disorder (systemic lupus erythematosus) |
Causes of Arthritis
The causes of arthritis are not simple. They come from a mix of our genes, things around us, and choices we make in life. We don’t always know exactly why someone gets arthritis. But we do know some things that make it more likely.
Genetics: Your genes are a big part of getting arthritis. Getting certain genes can make joints inflamed and prone to damage. If someone in your family has arthritis, you might be more at risk too.
Age: Getting older is a big risk for arthritis. As we age, our joints wear down, especially the cartilage, which can lead to osteoarthritis. This is the most common type.
Joint Injuries: Injuries to joints in the past can up the chance of arthritis in that joint. It’s because injuries can make the joint unstable, changing how it works. Also, cartilage might wear out faster.
Metabolic Diseases: Diseases that affect our metabolism, like diabetes, and being overweight have a connection to arthritis. They can cause swelling and damage to joints over time.
Sociodemographic Factors: Things like your age and gender also play a part in arthritis. Women often get rheumatoid arthritis more, while osteoarthritis is common in older people. It often affects the hips and knees the most.
Prevention Strategies: Even though arthritis has many causes, there are ways to lower your risk. Keeping a healthy weight is key. Extra weight puts more stress on your joints, especially the hips and knees. Being active can keep your joints moving well and help avoid obesity. And don’t forget, you should also be careful about overdoing activities that may harm your joints.
Risk Factors for Arthritis
| Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetics | Inherited genetic factors that increase the likelihood of developing arthritis |
| Age | Older age is associated with an increased risk of developing arthritis |
| Joint Injuries | Previous joint injuries, fractures, or dislocations can contribute to the development of arthritis |
| Metabolic Diseases | Conditions like diabetes, obesity, and gout can increase the risk of arthritis |
| Sociodemographic Factors | Age and gender can influence the likelihood of developing arthritis |
Knowing the causes and risks of arthritis lets you take steps to lower your risk. A healthy lifestyle and keeping to a normal weight are important. So is being smart about protecting your joints. These things together can help keep arthritis away and make your joints feel better, giving you a better life.
Prevention and Control of Arthritis
Prevention is key in dealing with arthritis and making it less of a daily bother. You can avoid arthritis by being careful with your joints and staying healthy. It’s all about not overdoing it and making good lifestyle choices.
Reducing Joint Overuse
Arthritis can often be avoided by not using your joints too much. People who do a lot of hard, repetitive work or play intense sports should be especially careful. This prevents joint damage and keeps inflammation at bay.
It’s important to balance your exercise to avoid joint stress. Taking breaks, changing how you work out or at work, and using the right equipment all help. These steps protect your joints over time.
Promoting a Healthy Lifestyle
Living healthy is key to staying away from arthritis and managing it if you have it. Regular, light exercise keeps joints and muscles strong, and it boosts your mood. Activities like swimming, biking, or yoga are great for your joints.
It’s also important to keep your weight in check. Extra pounds stress your joints, which could lead to arthritis in knees and hips. Eat right and watch your portions to maintain a healthy weight.
Learning and counseling can also help you keep arthritis in check. These give you tips to manage your symptoms and make work easier on your joints. The goal is to prevent any more joint harm.
Getting diagnosed early and starting a plan just for you are crucial. This way, doctors can keep an eye on your joint health and adjust treatment as needed. Regular visits help them fine-tune your care and keep your joints working as best as they can.

| Preventive Measures | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Reducing joint overuse |
|
| Promoting a healthy lifestyle |
|
| Educational programs and counseling |
|
| Early diagnosis and regular monitoring |
|
Diagnosis of Arthritis
Diagnosing arthritis involves looking deeply into a patient’s medical history. It also includes a physical check-up, lab tests, and imaging. This helps doctors figure out the kind and level of arthritis someone has.
The doctor begins by asking about the patient’s symptoms. This includes things like joint pain, stiffness, and if they’re swollen. Learning about these symptoms is a big step in the diagnostic process.
The examination checks for signs like joint tenderness or swelling. The doctor will move the joints to see if there are any limits in motion. These steps help them know if the patient has arthritis, and how severe it might be.
Blood tests are key to diagnosing arthritis. They check for high levels of things like CRP and ESR, which show inflammation. Other tests can look for autoimmune diseases linked to arthritis.
Using imaging like X-rays and MRIs helps doctors see inside the joints. These tests show the condition of the bones and cartilage. They might also reveal issues like bone spurs.
Sometimes, a sample of joint fluid is needed for tests. This is called arthrocentesis. It helps identify the cause of inflammation, like an infection.
Common Diagnostic Tests for Arthritis
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Medical History | Evaluate symptoms and identify potential risk factors |
| Physical Examination | Assess joint inflammation, mobility, and functionality |
| Blood Tests | Detect markers of inflammation and autoimmune diseases |
| Imaging Studies (Ultrasound, X-rays, MRI, CT scans) | Visualize joints, assess cartilage condition, detect abnormalities or damage |
| Joint Fluid Aspiration (Arthrocentesis) | Analyze synovial fluid for the diagnosis of infection or crystal-related arthritis |
A comprehensive approach is crucial for diagnosing arthritis. It helps create the best treatment plan for each patient. With correct diagnosis, managing arthritis becomes more effective, leading to a better life for those affected.
Treatment and Management of Arthritis
Arthritis is managed carefully with each person’s needs in mind. It includes many ways to lessen pain, improve joints, and boost health.
Medication for Pain and Inflammation Control
Medicine is key in treating arthritis. Drugs like NSAIDs and DMARDs handle pain and lower swelling. This can make a big difference in moving and feeling better.
Physical Therapy for Joint Function Improvement
Physical therapy helps a lot. It uses exercises and stretches to make joints work better. This can lower pain and increase how much you can move.
Assistive Devices for Support and Stability
Using items like braces can support sore joints. They take away some pain and prevent more harm. Health pros will find or make the right one for you.
Lifestyle Modifications for Arthritis Management
Changing how you live can lessen arthritis. Keeping a good weight, eating right, and moving often are vital. Simple changes in daily tasks can also save your joints from wear and tear.
Joint Replacement Surgery for Severe Cases
If arthritis is really bad, surgery might help. This includes getting a new joint, like a hip or knee. It’s done to end pain and boost movement.
Self-Care Strategies for Arthritis Management
Taking care of yourself is crucial. Knowing and coping with arthritis is tough but can be learned. Active living, good weight, and talking about your feelings make a big difference.
Comparison of Arthritis Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Description | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Medication | Prescribed drugs for pain and inflammation control | Relief from pain and improved joint function |
| Physical Therapy | Exercises and activities to improve joint functionality | Increased strength, flexibility, and mobility |
| Assistive Devices | Braces or splints for support and stability | Pain reduction and prevention of further damage |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Healthy weight management and activity modifications | Reduced joint strain and improved overall joint health |
| Joint Replacement Surgery | Surgical replacement of damaged joints | Pain relief and restoration of joint functionality |
To fight arthritis, a mix of treatments works best. This includes medicine, therapy, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery. Living healthily and staying active can make a good difference.
Self-Care for Arthritis
Self-care is crucial for people with arthritis. Learning about the condition and getting support can make a big difference. They help deal with both the physical and emotional aspects. It’s important to stay active to ease symptoms and slow down the disease. Also, keeping a healthy weight lessens the strain on your joints.
Some vital self-care strategies can make living with arthritis easier. Let’s look at a few that are often recommended:
- Exercise is key: It should be designed for each person’s ability. Regular physical activities keep joints flexible, muscles strong, and pain low. Swimming, cycling, and yoga, which are gentle on the joints, are great choices.
- Physical therapy and exercises can help a lot. A physical therapist can show you exercises to improve movement in your joints. These target pain reduction, strength building, and increase your ability to move.
- Follow a balanced diet: Eating plenty of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins is essential. Some foods, like fish, which has omega-3 fatty acids, can help lessen inflammation.
- Dealing with stress is really important. Stress can make arthritis symptoms worse. Finding ways to relax, like deep breathing, meditation, or hobbies, can lower stress levels.
- Use aids if needed: Certain devices like braces, splints, or canes can help. They reduce joint pressure and make moving easier.
It’s best to create a personalized care plan with your healthcare provider. They can give you advice suited just for you, suggest therapies, and check how you’re doing. Following these self-care tips helps you take control of your arthritis. It leads to a better life and overall health.
WHO’s Response to Arthritis
The World Health Organization (WHO) thinks it’s vital to help people with arthritis. They’ve started programs like Rehabilitation 2030 and the UN Decade of Healthy Ageing. These efforts aim to make care and support easier to get for those with arthritis.
Rehabilitation 2030 is all about making sure people with arthritis can age healthily. It makes them the focus, with tailored health and social care plans. These plans help improve their life and let them play an active role in society.
WHO says that rehab is key for dealing with arthritis. It combines things like physical and occupational therapy to help people move better and feel less pain. They also focus on providing tools and technology to boost independence and daily activity.
WHO is serious about making arthritis care better. They want to ensure that everyone with arthritis gets the right help to live a better life.
Modern Methods of Treatment for Arthritis
New treatments like stem cell therapy are offering hope for arthritis patients. Stem cells are special because they can become many different types of cells. In the case of arthritis, they might help make damaged joints better, reducing pain and swelling.
Doctors mainly use mesenchymal stem cells for treating arthritis. These cells come from sources like bone marrow or fat. When these MSCs are put into a sore joint, they might help grow new cartilage and make the joint feel better.
Studies show that stem cell therapy could really help people with arthritis. It might even fix some of the joint damage. But, this area of medicine is still young. More studies are required to know for sure how well it works over time.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Arthritis
Stem cell therapy can be a good choice for many reasons:
- Pain reduction: Stem cells might lower the pain of arthritis by decreasing inflammation.
- Promotes tissue repair: Their ability to repair damaged joints and build new cartilage is quite promising.
- Minimally invasive: It’s a surgery-free option that can be done quickly, lowering the risk level.
- Reduced reliance on medication: It aims to lower the need for drugs used for controlling arthritis symptoms.
Even with these benefits, it’s best to speak with a specialist before trying stem cell therapy. They can help choose the right treatment for you.
Risks and Considerations
Understanding the possible downsides to stem cell therapy for arthritis is vital:
- Effectiveness: Not everyone might see the same benefits. How well it works can depend on different health and disease factors.
- Cost: This therapy can be costly, and not all insurances will cover it. It’s important to think about the financial impact.
- Regulation: Stem cell use for arthritis is still quite new, and rules may differ by location. Make sure to go to a trusted clinic that follows the correct standards.
- Long-term effects: Given that it’s a new treatment, we’re still learning about its lasting effects. Doctors need to discuss these points well with their patients.
Conclusion
Arthritis, especially osteoarthritis, affects many people globally, causing pain and stiffness. It makes daily activities hard. Current treatments aim to manage symptoms and prevent more joint damage. Yet, newer methods such as stem cell therapy show promise in managing arthritis.
Stem cell therapy uses cells from sources like bone marrow to heal and ease joint inflammation. Despite its promising effects, we still need more studies to ensure its safety, how well it works, and its lasting benefits.
By focusing on prevention, early diagnosis, and a full approach to care, arthritis patients can enjoy a better life. A diverse approach to arthritis care includes drugs, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. It also involves exploring new treatments like stem cell therapy. This approach helps people with arthritis move better, reduce pain, and feel healthier in general.