Appendicitis is a common problem that needs quick attention. It’s when the appendix is swollen. Symptoms include belly pain, fever, and tummy trouble. Doctors find it with exams, blood work, or scans. The main fix is to take out the bad appendix. But, some look into using stem cells to help.
Key Takeaways:
- Appendicitis is a common surgical emergency characterized by inflammation of the appendix.
- Symptoms include abdominal pain, fever, and digestive disorders.
- Diagnosis involves clinical examination, blood tests, and imaging methods like ultrasound or CT scans.
- The main treatment is surgical removal of the inflamed appendix.
- Stem cell therapy is being explored as a potential alternative or complementary treatment.
What is Acute Appendicitis?
Acute appendicitis means the appendix is suddenly very inflamed. This often happens when something blocks the appendix. The blockage allows bacteria to grow and the appendix to swell. If not taken care of, the appendix can burst. This lets pus go into the stomach and can cause a serious sickness called peritonitis.
Symptoms of Appendicitis
Appendicitis is tricky to diagnose because it has many symptoms. Knowing these signs can help spot the problem early. This leads to quicker medical care.
1. Abdominal Pain
Appendicitis often starts with pain. This pain usually begins near the belly button. Then it moves to the lower right side. The pain can get really bad, becoming sharp and intense. It might even hurt more when you move, cough, or sneeze.
2. Abdominal Tenderness
One key sign of appendicitis is a tender belly. Pushing gently on the lower right side can hurt. Doctors check for this pain using a test named after a doctor, called McBurney’s point tenderness test.
3. Fever
A fever is often a sign of something serious like appendicitis. If your body temperature is over 100.4 °F (38 °C), it could be a problem. A fever that sticks around suggests an infection or inflammation.
4. Loss of Appetite
Not feeling hungry is a common symptom of appendicitis. You might also feel generally unwell. This could be because the belly feels uneasy or off.
5. Digestive Disorders
In addition to a loss of appetite, digestive issues might arise. You could feel sick, throw up, or have diarrhea. This could be because the appendix swelling up messes with your digestion.
If you notice these symptoms, don’t wait. It’s essential to see a doctor soon. They can check what’s wrong and suggest the best treatment.
Table: Comparison of appendicitis symptoms
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Abdominal Pain | Pain starting from the umbilicus or epigastrium and moving to the lower right abdomen. |
| Abdominal Tenderness | Discomfort or pain when pressing on the lower right abdomen. |
| Fever | Elevated body temperature above 100.4 °F (38 °C). |
| Loss of Appetite | Diminished desire to eat. |
| Digestive Disorders | Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. |
Causes of Appendicitis
Appendicitis can happen for many reasons. This includes appendix obstruction, enlarged lymph nodes, foreign bodies, and tumors. A common cause is when the appendix’s path is blocked. This block is often because of fecal matter or large cysts.
Sometimes, foreign bodies like seeds can also block the appendix. Occasionally, tumors in the appendix can lead to appendicitis.
This block stops the appendix from getting rid of fluid and waste. As a result, it becomes inflamed. This causes pain, fever, and digestive issues.
The causes of appendicitis are summarized in the table below:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Appendix Obstruction | Blockage due to fecal stones or large lymphatic cysts |
| Foreign Bodies | Entry of objects that block, like fruit seeds |
| Tumors | When tumors obstruct the appendix or cecum |
Remember, the cause of appendicitis can be different for each person. Sometimes, a cause isn’t found.
Obstruction and Inflammation
Appendix blockage often starts appendicitis. It’s when something stops the appendix from working properly. This blockage causes fluid and bacteria to build up, leading to inflammation.
Almost 80% of appendicitis cases are due to this blockage. The appendix can’t drain, and inflammation causes the sickness.
Foreign Bodies and Tumors
Foreign bodies like seeds can get stuck, leading to inflammation. They can also block the way out for the appendix’s fluid, causing infection.
Also, tumors in the appendix or nearby can block it. This blockage irritates the appendix, causing appendicitis symptoms.
Diagnosis of Appendicitis
Doctors figure out if you have appendicitis using exams, blood tests, and images. These steps are key to confirm the disease. They also help choose the right treatment.
Clinical Examination
When you see a doctor, they look at your symptoms and feel your stomach. They focus on where it hurts and if there’s any swelling. This helps them guess if it might be appendicitis.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are important in appendicitis diagnosis. They can show if you have an infection. A CBC test checks your white blood cell count. High numbers could mean you’re fighting an infection, which might be appendicitis.
Imaging Methods
Doctors use ultrasound and CT scans to see your appendix.
Ultrasound: It uses sound waves to make pictures of your insides. This safe test can find issues in your appendix.
CT Scan: CT scans give detailed pictures of your stomach and pelvis. They provide a clear view of your appendix. This helps confirm if you have appendicitis, especially in confusing cases.
Putting together exams, blood tests, and images, doctors can diagnose appendicitis well. A quick diagnosis is key to avoiding problems and getting the right care for this urgent surgery.
Treatment of Appendicitis
The main way to treat appendicitis is by removing the infected appendix. Doctors call this surgery “appendectomy.” The choice between open and laparoscopic surgery depends on how bad the infection is and the patient’s health.
During open surgery, the surgeon makes a cut in the stomach. They can see and remove the appendix directly. This method is better for serious cases or if there could be problems.
Laparoscopic surgery, though, is a kinder way to operate. It uses small cuts and special tools. A camera shows the appendix on a screen. This way, the surgery leaves smaller scars, hurts less, and heals quicker.
After surgery, the doctor might also give antibiotics. These medicines stop infections or help heal the appendix without surgery. The type and length of antibiotic use will vary from person to person, depending on their health.
Below is a table showing how open and laparoscopic surgeries differ:
| Open Surgery | Laparoscopic Surgery |
|---|---|
| Single incision | Small incisions |
| Direct visualization of appendix | Visualization through a camera |
| Recommended for complex cases | Minimally invasive approach |
| Longer recovery period | Shorter recovery period |
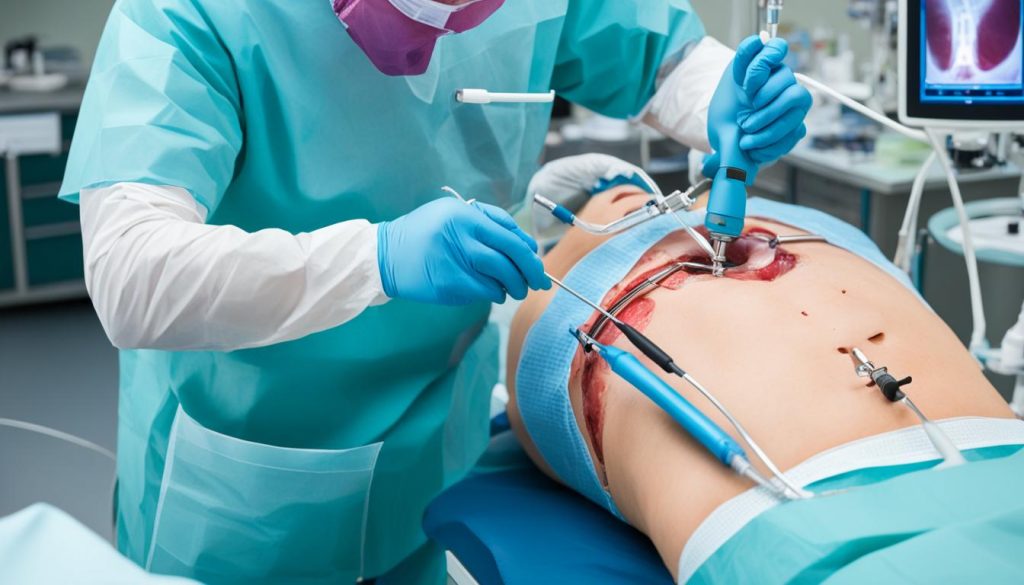
Speaking with a doctor is crucial to pick the right treatment. Both surgeries work well, and problems are not common.
Read on in Section 7 to understand the risks of appendicitis and why treating it promptly is vital.
Complications of Appendicitis
If appendicitis isn’t treated, it can cause serious problems. This might make later surgery necessary. These issues can really harm the patient’s health.
1. Appendiceal Abscess
One complication is an appendiceal abscess. It’s when pus gathers in the appendix. This can cause pain, swelling, and tenderness in the belly. You might also get a low fever and feel sick.
2. Peritonitis
Peritonitis is a dangerous complication. It’s caused by the inflammation of the abdominal cavity. When the appendix bursts, it can spread bacteria and pus. This leads to severe pain, fever, sickness, and vomiting. It’s a medical emergency needing quick treatment.
3. Intestinal Adhesions
After an appendicitis attack, intestinal adhesions may form. These are scar bands that can twist or block the intestines. They might cause cramps, bloating, constipation, or blockage. Sometimes surgery is needed to fix this.
To avoid complications like an abscess, peritonitis, or adhesions, early treatment is key. Getting appendicitis diagnosed and treated quickly is important for the patient’s health.
Stem Cell Therapy for Appendicitis
Stem cell therapy is a new way to possibly treat appendicitis. It uses the body’s stem cells to fix damaged areas. This could help by reducing inflammation and healing the appendix.
Scientists are working hard to see if this treatment is safe and works for appendicitis. They want to learn how stem cells can repair the appendix when it’s inflamed.
Thailand is a well-known place for cutting-edge medical treatments. It’s a top pick for those looking into stem cell therapy for appendicitis. This is because of their advanced clinics and experts in regenerative medicine.
To picture how stem cell therapy could help with appendicitis, check out this table:
| Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Appendicitis |
|---|
| Potential Reduction of Inflammation: Stem cells have regenerative properties that may help decrease inflammation in the appendix. |
| Promotion of Tissue Healing: Stem cell therapy aims to stimulate the healing process in the appendix, aiding in its recovery. |
| Minimally Invasive Procedure: The procedure for stem cell therapy is typically minimally invasive, offering a less invasive alternative to traditional surgical approaches. |
| Potential for Reduced Recovery Time: Stem cell therapy may result in a shorter recovery period compared to surgical removal of the appendix. |
We’re still learning about how effective and safe stem cell therapy is for appendicitis. Clinical trials are testing its benefits and safety. They’re key to understanding if this new method works well.
Appendicitis in Pregnant Women
Figuring out appendicitis in pregnant women can be tricky. This is because its signs can look like regular pregnancy pains. The appendix’s position might alter during pregnancy too.
Pregnant women with appendicitis might feel pain in their belly. If this pain stays and is on the right side, think about appendicitis. Be on the lookout for a fever, not eating much, and tummy issues.
Diagnosis Challenges
Spotting appendicitis in a pregnant woman needs a close look. The appendix might move, making symptoms confusing. This can delay diagnosis, which is risky.
Being pregnant can feel like having a tummy ache, feeling sick, or having different bathroom habits. This makes it hard for doctors to tell. They need to be extra careful and check things very well.
Doctors must be suspicious and check the patient carefully for appendicitis signs. This includes feeling the belly, checking temperature, and learning about past health.
Surgical Intervention
If appendicitis is likely, early surgery is best. This prevents problems for both the mom and the baby. Taking out the appendix through surgery is standard.
Doctors consider how bad the symptoms are and the stage of pregnancy. Sometimes, a type of surgery that’s less invasive and has a faster recovery is chosen.
Risks and Considerations
But, surgery during pregnancy has risks. Using CT scans for diagnosis might not be the best idea as it could harm the baby. Doctors carefully choose treatments that are safe.
They decide on imaging based on what’s safest for the baby. Sometimes, safer tests like ultrasound or MRI are used. They have less risk for the baby.
| Risk Factors | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Timing of surgery | Performed promptly to minimize the risk of complications |
| Anesthesia | Carefully selected to ensure the safety of both the mother and the fetus |
| Preterm labor | Appropriate monitoring and management to prevent preterm delivery |
| Post-operative care | Close monitoring to detect any signs of infection or complications |
Doctors and the mom work together for the best care. They focus on what’s safest for her and the baby. Detailed care and always checking are crucial for treating appendicitis in pregnant women.
Recurrence of Appendicitis
Even though appendicitis recurrence is rare, people should know it’s possible. Some factors make it more likely to happen again. These are:
- A history of previous appendicitis episodes
- Having certain underlying medical conditions that may contribute to appendiceal inflammation
- Surgical complications, such as poor wound healing or residual infection
After having an appendectomy, watching for any new symptoms is crucial. This means visiting the doctor regularly. They will check how you’re healing and if there are any issues. Early signs of appendicitis returning include stomach pain, fever, and problems eating. Good follow-up care helps catch these signs early. Then, the right care can be given fast, lessening problems.
Keeping an eye on your health after surgery is key. With proper care, the chance of appendicitis coming back is lower. This approach also makes your recovery smoother.
Care and Recovery after Appendectomy
After an appendectomy, careful care is vital for healing. Follow the post-appendectomy care closely for the best recovery.
Pain Management
Pain management is a big topic after appendectomy.
Your doctor might give you painkillers to ease the discomfort. Always take them as you’re told. If the pain is too much or doesn’t go away, talk to your doctor right away.
Activity Restrictions
After surgery, stick to your activity restrictions. Avoid things like heavy lifting and hard exercise. Your body needs time to heal.
Listen to your doctor’s advice on how long to take it easy. This helps prevent problems and makes your recovery smoother.
Wound Care
Taking care of your surgical wound is key. Clean and treat it just like your doctor showed you. Keep the wound dry.
If it gets wet, or you see redness, swelling, or pus, call your doctor right away.
Follow-up Appointments
Keep up with your follow-up appointments after surgery. Your doctor needs to check on how you’re healing and any problems that might come up.
It’s important to show up for these visits. Tell your doctor if anything doesn’t feel right before your next appointment.
Post-Appendectomy Care Summary:
- Follow the post-operative care instructions from your doctor.
- Use the pain medications as prescribed.
- Skip tough activities and don’t lift anything heavy for a while.
- Clean your surgical wound well to keep away infections.
- Go to all your follow-up appointments with your doctor.
Remember, each person’s recovery is different. Always listen to your body. And, stick close to your doctor’s advice for the best results.
Conclusion
Appendicitis is a common and urgent health issue that affects many people. The main treatment is surgery to remove the appendix. This surgery is very effective in stopping symptoms and preventing future issues.
Right now, there’s a lot of interest in using stem cell therapy to treat appendicitis. Scientists are studying if stem cell therapy could help as a new or add-on treatment. They want to make sure it’s safe and really works. This means there’s a chance we might see new ways to deal with this condition in the future.
After the surgery, taking good care of yourself is key to getting better. Listening to what your healthcare provider tells you about pain, caring for your wound, and what activities you can do is important. This helps your body heal and keeps any problems in check.
Visiting your doctor as they advise is also critical. They will check on how well you’re healing and can help with any worries. Looking forward, there’s a lot of hope that new developments in regenerative medicine will offer even better ways to treat appendicitis. Research and innovation could bring about treatments that are not only more effective but also less tough on patients. As we learn more, keeping up with the latest news in how to treat appendicitis is important.