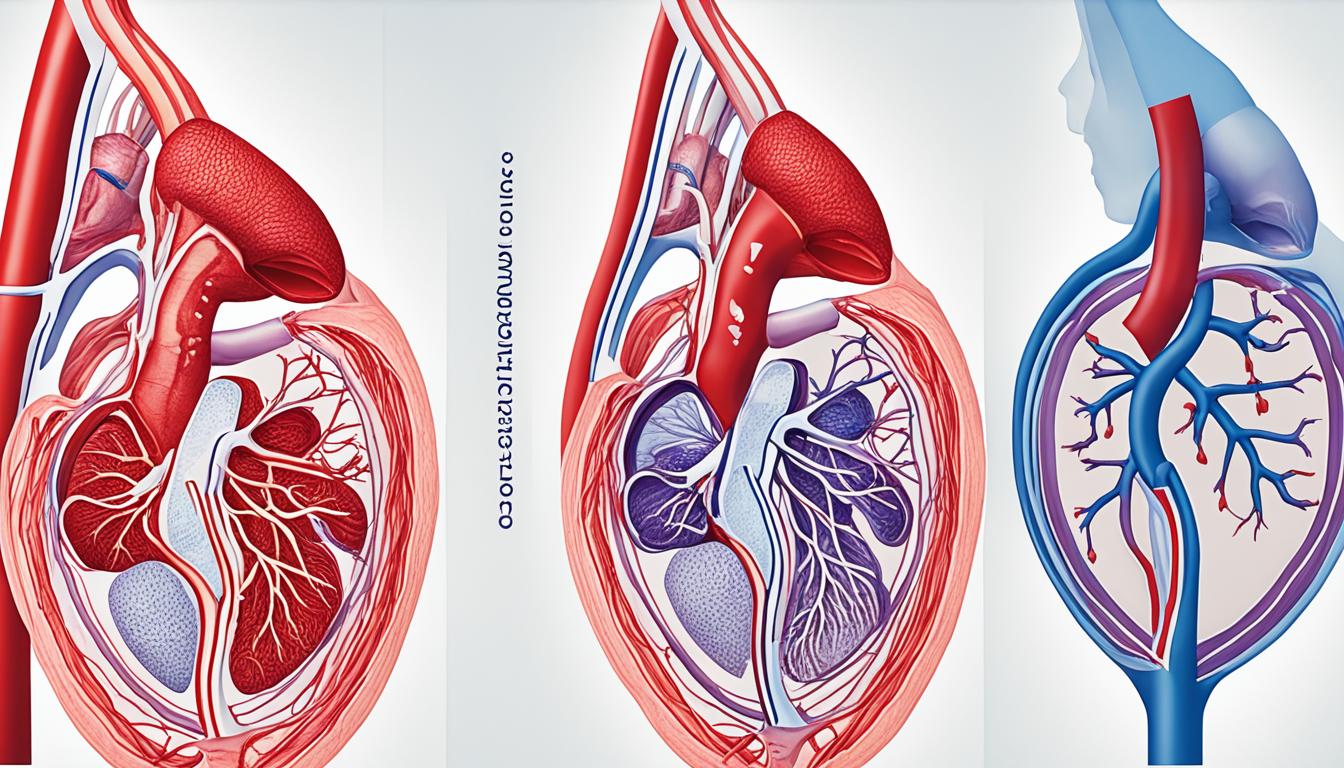
Aortic aneurysm is a condition where the aorta enlarges in some areas. This includes different parts like the ascending, arch, and abdominal aorta. It might not show any symptoms or cause chest pain, difficulty breathing, or fainting. The exact reason behind aortic aneurysm isn’t completely clear yet. But, getting older, smoking, high blood pressure, and certain genetic factors can make you more likely to have it.
Doctors use imaging tests like CT or ultrasound to diagnose aortic aneurysms. If the aneurysm is at risk of bursting, surgery or endovascular repair might be needed. A newer method, stem cell therapy, is being studied as a potential treatment for aortic aneurysms.
Key Takeaways:
- Aortic aneurysm is a chronic condition characterized by the localized expansion of the aorta.
- Symptoms of aortic aneurysm can include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fainting.
- Risk factors for aortic aneurysm include age, smoking, hypertension, and genetic conditions.
- Diagnosis of aortic aneurysm is typically done through imaging tests such as CT scans or ultrasounds.
- Treatment options for aortic aneurysm include surgical repair, endovascular repair, and stem cell therapy.
Understanding Aortic Aneurysm: Pathology and Mechanisms
Aortic aneurysm is a complex issue. It has many steps, like the breakdown of cells and inflammation. The way the aorta’s wall changes is really important. The wall’s strength and stretch ability lessen, causing an aneurysm to form.
Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) are very important in this. They can change and help make an aneurysm. Normally, these cells keep the aorta strong. But in an aneurysm, they become different and the wall gets weaker.
Inflammation is also a big factor. Cells gather and become active in the aorta, causing the release of harmful substances. These substances add to the swelling and changes in the artery’s wall. Inflammation working with VSMCs starts and continues the disease.
All these parts work together to create an aortic aneurysm. Knowing how they interact can show us how to stop or cure it. This insight is key for making medicines that work directly on the disease.
Figure 1: Illustration of aortic aneurysm pathology
Risk Factors for Aortic Aneurysm
Several factors can make the chance of getting an aortic aneurysm higher. Knowing these risk factors lets people lower their risk. The main factors for aortic aneurysm are:
Age:
Getting older is a big risk for aortic aneurysm. The aorta’s walls get weaker with age, making aneurysms more likely.
Smoking:
Smoking is a major cause of aortic aneurysm. The chemicals in cigarettes can harm the aorta’s walls. This damage can lead to an aneurysm. So, stopping smoking is key to lowering your risk.
Hypertension:
High blood pressure is a key factor for aortic aneurysms. It puts extra stress on the aorta’s walls over time. This can make an aneurysm more likely.
Genetic Conditions:
Genetic issues like Marfan syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome can increase aortic aneurysm risk. They can make the aortic walls weaker because of issues with the connective tissue.
To lower your aortic aneurysm risk, you should lead a healthy life. This includes not smoking, managing your blood pressure, and talking to a doctor about your genetics if needed.
| Risk Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | Incidence increases with advancing age |
| Smoking | Strongly linked to aortic aneurysm development and progression |
| Hypertension | Puts increased pressure on the arterial walls, including the aorta |
| Genetic Conditions | Predispose individuals to aortic aneurysm due to connective tissue abnormalities |
Diagnosis and Screening of Aortic Aneurysm
It’s really important to diagnose aortic aneurysms early to treat them well. Doctors use advanced tests like CT scans and ultrasounds for this.
CT scans show clear pictures of the aorta. This helps doctors know how serious the aneurysm is. They look closely at size, shape, and where it is. Then, they can choose the best treatment.
Ultrasounds are great too. They let doctors look at the aorta and see the aneurysm’s size. It’s a safe test that uses sound waves for pictures.
Some people have a bigger chance of getting aortic aneurysms. For them, regular tests are a smart idea. These tests check for any aneurysm growth or new ones.
Early detection is key to treating aortic aneurysms safely. With regular checks, problems can be found sooner. This leads to better health results.
Treatment Options for Aortic Aneurysm
The treatment for aortic aneurysm depends on the size and where it is. Also, how healthy the person is matters. There are three ways to treat it: surgical repair, endovascular repair, and stem cell therapy.
Surgical Repair
Surgical repair replaces the damaged part of the aorta with a synthetic graft. This surgery needs a big cut in the chest or abdomen. The sick part of the aorta is taken out. Then, a synthetic graft is stitched in to make the aorta strong again. Surgeons do this for big aneurysms or ones that are growing quickly and might burst.
Endovascular Repair
Endovascular repair is less invasive. It uses a stent graft to support the aorta’s weak part. A doctor puts a catheter in the body through a small cut in the groin. Then, guided by X-ray, they place the stent graft at the aneurysm. This makes a new way for blood to flow, helping to protect the weak area. It’s a good choice for older or less healthy patients who can’t have open surgery.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is new. It uses stem cells to try to heal the aortic wall. Early studies are promising. They suggest it might reduce the risk of the aneurysm getting worse or bursting. But, we need more research to know if it’s safe and effective.
Choosing a treatment is a personal choice. It’s best to talk with your doctors. Surgical and endovascular repairs are commonly used. Stem cell therapy is an exciting area for the future.
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Surgical Repair | Replacement of the affected portion of the aorta with a synthetic graft through open surgery. |
| Endovascular Repair | Placement of a stent graft inside the aorta to reinforce the weakened wall through a minimally invasive procedure. |
| Stem Cell Therapy | Utilization of stem cells to promote tissue regeneration and repair in the aortic wall. |
Complications and Prognosis of Aortic Aneurysm
Aortic aneurysm can cause problems that seriously affect health. Knowing these risks helps in treating it well.
Aortic Rupture
If the aortic wall tears, it’s a medical emergency. Immediate surgery is needed to prevent worse outcomes.
Aortic Dissection
Aortic dissection happens when the aorta’s layers separate, creating a false channel. This can lead to aortic rupture if not fixed.
Aortic Thrombosis
Blood clots near the aneurysm can cause serious issues. They may block blood flow or travel, causing strokes or organ damage.
Prognosis of Aortic Aneurysm
The chances of recovery depend on the aneurysm’s size, where it is, and your health. Bigger aneurysms have a higher risk of bursting.
Detecting it early and managing it well is key. Keeping an eye on its size and health measures like controlling blood pressure can help a lot.
Knowing the risks and outcomes of aortic aneurysm is key to managing it well. Good care and regular checks can make a big difference in living with it.
| Complications | Description |
|---|---|
| Aortic Rupture | Tearing or bursting of the weakened aortic wall, leading to life-threatening bleeding. |
| Aortic Dissection | Separation of the layers of the aortic wall, potentially causing aortic rupture. |
| Aortic Thrombosis | Formation of blood clots within or near the aneurysm, with the risk of embolism. |
Prevention and Lifestyle Strategies for Aortic Aneurysm
Aortic aneurysms may not always be preventable, but a healthy lifestyle helps lower the risk. Several strategies boost cardiovascular health and cut down risk factors:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. These foods keep your heart healthy by providing important nutrients.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being at a healthy weight is good for your heart and blood vessels. It lowers the strain they face, which reduces the risk.
- Engage in Regular Exercise: Activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling are great for your heart. They make blood vessels stronger and improve overall heart fitness.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk for aortic aneurysm. It’s crucial to stop smoking to lower your chances of getting it.
- Manage Blood Pressure: Keep an eye on your blood pressure and work with your doctors. It’s essential for both preventing and slowing the aneurysm’s progress.
Leading a healthy life can drop your chances of getting an aortic aneurysm. Focus on quitting smoking and keeping your blood pressure in check. These steps are key in preventing an aneurysm.
The advice here is general and not a substitute for personal medical advice. Always talk to a doctor for advice that fits your health situation.
| Prevention and Lifestyle Strategies for Aortic Aneurysm | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Eat a Balanced Diet | Provides essential nutrients for cardiovascular health |
| Maintain a Healthy Weight | Reduces strain on the heart and blood vessels |
| Engage in Regular Exercise | Strengthens blood vessels and improves cardiovascular fitness |
| Quit Smoking | Significantly reduces the risk of aortic aneurysm |
| Manage Blood Pressure | Prevents the development and progression of aortic aneurysm |
Advances in the Management of Aortic Aneurysm
The way we treat aortic aneurysm has gotten much better in recent years. Now, stem cell therapy is showing big potential. It uses the power of stem cells to fix and regrow the aortic wall.
Aortic aneurysms happen when the aorta expands and weakens. This can make an aneurysm more likely to grow and burst. Stem cell therapy works to make new, strong tissue, making these risky spots stronger and less likely to cause problems.
Scientists think stem cell therapy could really change how we deal with aortic aneurysms. It could help the body make new tissue and prevent the aorta from getting worse.
Stem Cell Therapy for Aortic Aneurysm
Right now, we’re still studying how well stem cell therapy works for aortic aneurysms. Stem cells are special because they can help repair the aortic wall. This could be a good way to truly treat what’s going wrong in the body.
With stem cell therapy, scientists are aiming for better results for people with aortic aneurysms. They hope to use stem cells to grow new tissue. This might treat the real problem, lessening the need for big surgeries.
Still, there’s a lot we don’t know. More studies and tests are needed to see how well stem cell therapy works, and if it’s safe. Teams of experts are working together to figure this out, so we can find the best treatments.
| Treatment | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Surgical Repair | – Replaces the affected section of the aorta with a synthetic graft – Enhances the structural integrity of the aortic wall |
| Endovascular Repair | – Minimally invasive procedure – Reinforces the weakened aortic wall with a stent graft – Reduces the risk of aneurysm progression |
| Stem Cell Therapy | – Promotes tissue regeneration in the aortic wall – Aims to address underlying structural abnormalities – Potential for reducing the need for invasive interventions |
Conclusion
Aortic aneurysm is a serious health issue marked by the aorta getting bigger. It might have no symptoms or cause chest pain and breathing troubles. The reasons for aortic aneurysm are not all clear. But, things like age, smoking, high blood pressure, and certain genes make it more likely.
To find out if you have an aortic aneurysm, doctors do tests like CT scans and ultrasounds. These tests show how big the aneurysm is and where it is. Then, the right treatment plan can be made. For treatment, there are surgeries or less invasive options like using stem cells. Each has its good points and things to think about.
If not treated, aortic aneurysms can be very dangerous. But, acting quickly and lifestyle changes can help a lot. New treatments like stem cell therapy are promising. However, we still need more studies to know if they are truly safe and helpful.
In short, aortic aneurysm is a problem that needs more research and better treatments. By working on the risk factors, finding it early, and using new therapies, we can do better in managing this condition. This way, people with aortic aneurysm can have a brighter future.
FAQ
Q: What is aortic aneurysm?
A: Aortic aneurysm is a serious health issue. It means a part of the aorta grows too big. The aorta is the main artery in the body.
Q: What are the symptoms of aortic aneurysm?
A: This problem might not show any sign. But it can cause chest pain, short breath, and fainting in some people.
Q: What are the causes of aortic aneurysm?
A: Doctors are not sure what exactly causes it. But they know that getting older, smoking, high blood pressure, and family history play a big part.
Q: How is aortic aneurysm diagnosed?
A: Doctors use special tests to find it, like CT scans or ultrasounds.
Q: What are the treatment options for aortic aneurysm?
A: There are ways to fix it. You can have surgery or a less invasive treatment. A new method using stem cells is also being explored.
Q: What are the complications and prognosis of aortic aneurysm?
A: It can cause serious problems like the aorta tearing or getting blocked. How well a person does depends on many things, such as how big the aneurysm is and how quickly it’s treated.
Q: Can aortic aneurysm be prevented?
A: You can lower your chances of getting it by being healthy. This means eating right, not smoking, and staying at a good weight.
Q: What are the advances in the management of aortic aneurysm?
A: Newer treatments are focusing on using stem cells. They aim to repair the aorta by growing new tissue.