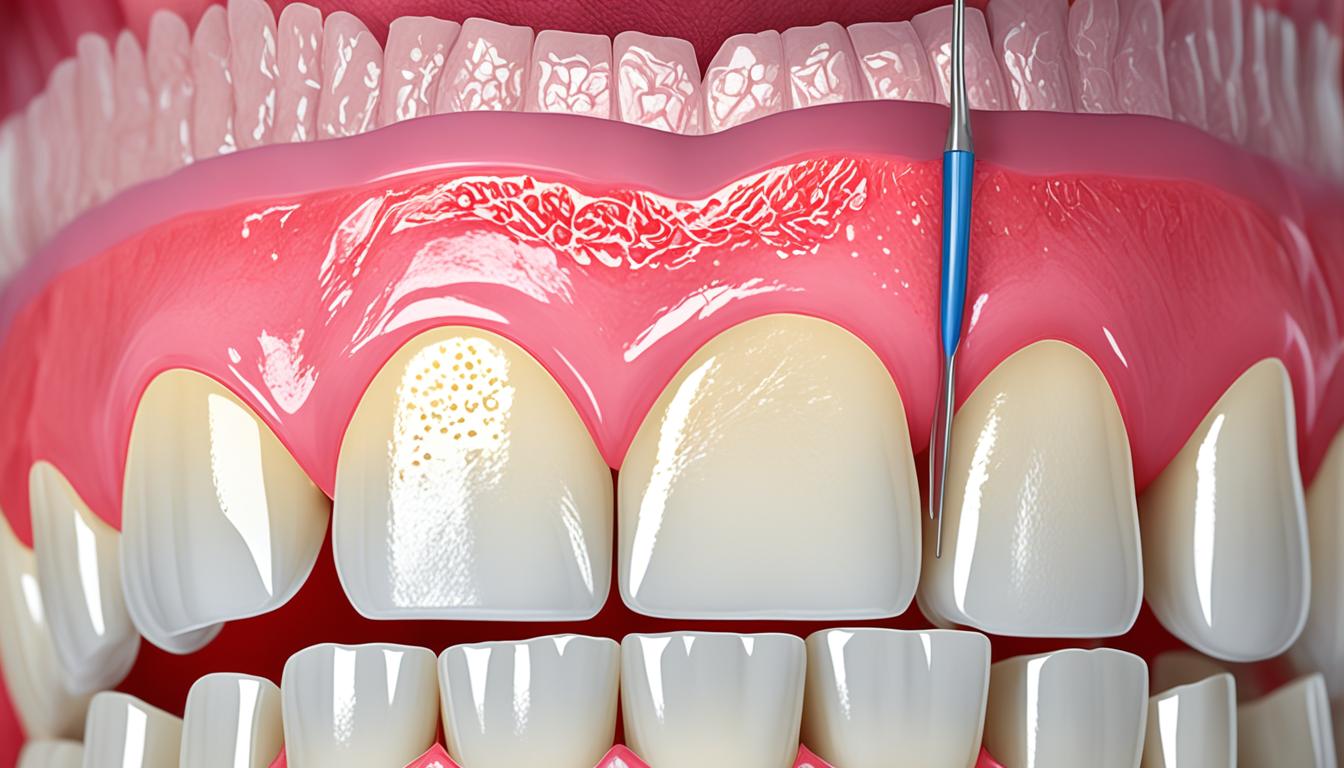
Gingivitis is a common gum disease that many people face. It causes gum inflammation and discomfort. Symptoms include swollen and bleeding gums. These can greatly affect oral and overall health.
The main culprits of gingivitis are plaque, bad dental hygiene, and more. These issues encourage bacterial growth. Bacteria cause gum inflammation, leading to gingivitis.
Diagnosing gingivitis requires a visit to a dentist. They will check your gums thoroughly. The dentist can spot gingivitis and decide how to treat it.
Stem cell therapy is a new treatment for gingivitis. It involves making fibroblast cells in a lab. Then, these cells are put into the gums. This promotes gum tissue repair. Stem cell therapy is showing good results in reversing gingivitis effects.
Key Takeaways:
- Gingivitis is a common gum disease characterized by gum inflammation.
- Common symptoms include swollen and bleeding gums.
- The causes are from things like plaque buildup and tobacco use.
- Diagnosing gingivitis requires a visit to a dentist.
- Stem cell therapy is a promising new treatment for gingivitis.
“Symptoms and Causes of Gum Recession”
Gum recession is when the gum tissue around teeth starts to pull back. This exposes the root of the tooth and creates gaps between gums and teeth. This can cause several dental issues and discomfort.
It often starts with tooth sensitivity. When the gums recede, the roots become exposed. So, eating hot or cold foods can cause pain or discomfort.
Other signs might include red, swollen, or bleeding gums, and teeth that look longer. Inflammation from recession causes red or swollen gums. Bleeding may happen when brushing or eating. With more of the tooth showing, they can seem longer.
Plaque and poor cleaning can lead to gum diseases that cause recession. Such diseases attack the gums, leading them to pull back.
Gum recession may also be from things like wrong brushing, hormones, or smoking. These habits and issues stress the gums, causing them to recede.
To prevent further issues, treat gum recession early. Regular dental visits and good habits like daily flossing can help. Quitting smoking and fixing tooth alignment can also lessen the chance of recession.
Common Causes of Gum Recession
| Causes | Description |
|---|---|
| Periodontal diseases | Plaque buildup and poor dental care can lead to inflammation and damage to the gum tissue. |
| Genetic factors | Some individuals may be more prone to gum recession due to genetic predispositions. |
| Incorrect brushing techniques | Aggressive brushing or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can cause gum tissue to recede. |
| Hormonal changes | Changes in hormone levels, such as during pregnancy or menopause, can affect the gum tissue. |
| Tobacco use | Smoking or using tobacco products can contribute to gum recession and other oral health problems. |
| Teeth grinding (bruxism) | Grinding or clenching the teeth can put pressure on the gum tissue, causing it to recede. |
| Misaligned teeth | Crooked or crowded teeth can create uneven pressure on the gums, leading to recession. |
| Lip or tongue piercing | Jewelry in the mouth can irritate and damage the gums, contributing to gum recession. |
“Treatment and Prevention of Gum Recession”
The level of gum recession guides its treatment. Choices range from simple actions to stop further damage to the gums.
Scaling and Plaque Removal
At first, scaling and plaque removal help. They clear away plaque and tartar under the gumline. This cleaning kills bacteria and lowers infection risks.
Gum Surgery
Advanced gum recession might need surgery. The type of surgery depends on how bad it is and the patient’s oral health. The goal is to cover tooth roots and help the gums grow back.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is new but promising for gum recession. It uses cells from the patient’s own gums. This method naturally restores gum health.
Dental Care
- Prevent gum recession with good oral care. This means brushing and flossing regularly to fight plaque.
- Mouthwash that kills bacteria can lower gum disease risks.
- Seeing a dentist often for cleanings and check-ups catches gum issues early.
Tobacco Cessation
Smoking or chewing tobacco harms gums. Stopping tobacco use is key to oral health and preventing gum recession.
Proper Tooth Brushing
Brush right to avoid gum recession. Use a soft brush and circle your teeth gently. Rough brushing can hurt your gums.
With good habits and timely care, gum recession can be controlled. This approach helps maintain healthy gums.
“Gingivitis in Cats and Treatment Options”
Cats can get gingivitis too. It makes their gums red and hurt. This dental problem is most common in older cats. It happens when bacteria and food bits build up in their mouth.
Treating cat gingivitis has many steps. First, a vet might clean the cat’s teeth. They remove plaque and tartar. Antibiotics can also be part of the treatment to fight off infection.
If the condition is really bad, a vet might suggest surgery. This could be pulling out teeth or removing gum tissue. These steps can stop the pain and the issue from getting worse.
To stop gingivitis in cats, preventing it is best. Have your vet clean your cat’s teeth regularly. Also, brush your cat’s teeth and use special products. A good diet is important too. Seeing the vet for check-ups can catch gingivitis early. This means your cat can get help sooner.
FAQ
Q: What are the symptoms of gingivitis?
A: Symptoms of gingivitis are easy to spot. You may notice your gums swollen or bleeding. You might also see they’re red and feel pain. Bad breath is also common.
Q: What causes gingivitis?
A: Plaque buildup is the main offender in gingivitis. But, bad oral care, hormonal shifts, smoking, and grinding your teeth can also lead to it. Even having teeth that don’t fit together well can play a part.
Q: How is gingivitis diagnosed?
A: Gingivitis is spotted by dentists, and the signs they look for are pretty clear. They check for inflamed, bleeding gums. Sometimes, X-rays are needed to see how far the problem has spread.
Q: What is stem cell therapy for gingivitis?
A: In this therapy, scientists make more fibroblast cells in labs. Then, they put these cells into the gums. The goal is to help the gums heal and grow stronger.
Q: What are the symptoms of gum recession?
A: You might have gum recession if your teeth are more sensitive or look longer. Your gums might also be red or bleed easily. Sometimes, this happens for no reason.
Q: What causes gum recession?
A: Periodontal diseases, genetics, and poor dental habits can lead to gum recession. Hormones, smoking, and even having teeth or tongue piercings increase the risk.
Q: How is gum recession treated?
A: The first steps usually involve cleaning and removing plaque. If the recession is bad, surgery might be needed. Stem cell therapy is also being explored as a treatment.
Q: How can gum recession be prevented?
A: Taking good care of your teeth is vital. This means brushing, flossing, and seeing the dentist often. Avoiding tobacco and fixing teeth that don’t fit correctly can also reduce your risk.
Q: Can gingivitis affect cats?
A: Yes, cats can get gingivitis too. You might notice their gums are sore and more swollen. This is often seen in adult or older cats.
Q: What causes feline gingivitis?
A: Feline gingivitis is often triggered by a build-up of plaque. Bacteria in this plaque can cause inflammation in a cat’s mouth.
Q: How is feline gingivitis treated?
A: To treat cat gingivitis, vets might clean their teeth or give them medications. In severe cases, surgery might be needed. Keeping your cat’s teeth clean and healthy is critical for preventing this issue.